ITER Cooperation
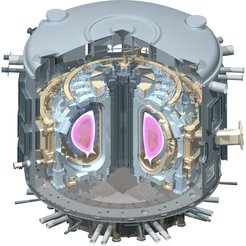
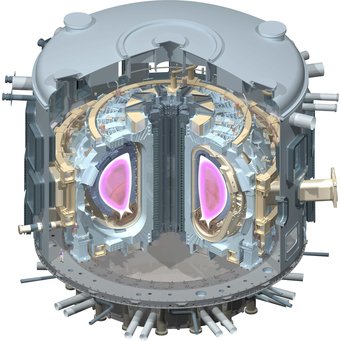
In the ITER project the world's major fusion programmes – those of Europe, Japan, the USA, the Russian Federation, China, South Korea, and India – are jointly constructing a first experimental reactor. ITER (latin "the way") is intended to show that it is physically and technically possible to gain energy from nuclear fusion. Its objective is to produce a burning, energy-yielding plasma for the first time.
ITER should release 500 megawatts of fusion power – ten times the heating power coupled in. Furthermore, it is to be used for developing and testing essential technical functions of a fusion reactor. These include superconducting magnetic field coils, tritium technology, exhaust of the thermal energy generated, and development of remotely replaceable components; the safety and environmental aspects of fusion will also be treated.
IPP and ITER
IPP is contributing to prepare and support ITER operations through the research programme being conducted on its ASDEX Upgrade fusion device. The ITER Technology & Diagnostics Division is responsible for IPP's technological development contributions to ITER: participation in the development of the neutral particle heating system and the development of various diagnostics for ITER. IPP staff are part of the international team developing the ITER plasma control system. IPP scientists are also maintaining close contact with the ITER group in many physics-oriented questions and are treating special problems for ITER in numerous contract studies.